-
Learning by doing
-
Trainers with practical experience
-
Classroom training
-
Detailed course material
-
Clear content description
-
Tailormade content possible
-
Training that proceeds
-
Small groups
In the course Hadoop for Big Data participants learn how to use Apache Hadoop for the storage and processing of large amounts of data.
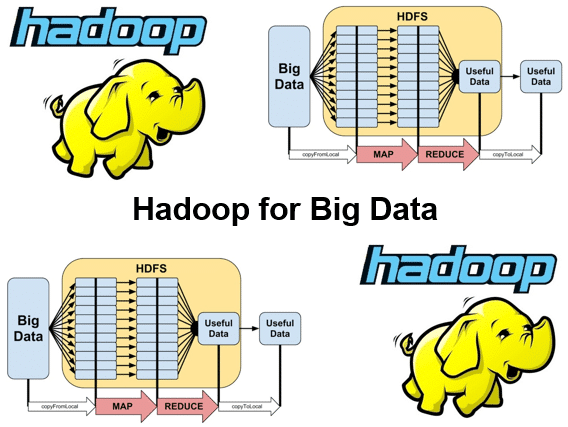
In the course Hadoop for Big Data the architecture of Hadoop is explained in depth. Hadoop uses a simple programming model in a distributed environment over a cluster of computers.
The Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is used as file system within a Hadoop cluster. In the course Hadoop for Big Data HDFS in explained in detail. HDFS is a horizontal scalable file system that is stored on a cluster of servers. The data is stored in a distributed manner and the file system automatically ensures replication of data over the cluster.
An important algorithm for the processing of data is the MapReduce algorithm and this is given extensive attention.
Finally attention is paid to tools and utilities that are often used in combination with Hadoop such as Zookeeper, Scoop, Ozie and Pig.
The course Hadoop for Big Data is intended for developers, data analysts and others who want to learn how to process data with Hadoop.
To participate in this course prior knowledge of programming in Java and databases is beneficial for the understanding. Prior knowledge of Java or Hadoop is not necessary.
The theory is treated on the basis of presentations. Illustrative demos are used to clarify the covered concepts. There is ample opportunity to practice and theory and practice are interchanged. The course times are from 9.30 to 16.30.
Participants receive an official certificate Hadoop for Big Data after successful completion of the course.
Module 1 : Hadoop Intro |
Module 2 : Java API |
Module 3 : HDFS |
|
Big Data Handling No SQL Comparison to Relational DB Hadoop Eco-System Hadoop Distributions Pseudo-Distributed Installation Namenode Safemode Namenode High Availability Secondary Namenode Hadoop Filesystem Shell |
Create via Put method Read via Get method Update via Put method Delete via Delete method Create Table Drop Table Scan API Scan Caching Scan Batching Filters |
Hadoop Environment Hadoop Stack Hadoop Yarn Distributed File System HDFS Architecture Parallel Operations Working with Partitions RDD Partitions HDFS Data Locality DAG (Direct Acyclic Graph) |
Module 4 : Hbase Key Design |
Module 5 : MapReduce |
Module 6 : Submitting Jobs |
|
Storage Model Querying Granularity Table Design Tall-Narrow Tables Flat-Wide Tables Column Family Column Qualifier Storage Unit Querying Data by Timestamp Querying Data by Row-ID Types of Keys and Values SQL Access |
MapReduce Model MapReduce Theory YARN and MapReduce 2.0 Daemons MapReduce on YARN single node MapReduce framework Tool and ToolRunner GenericOptionsParser Running MapReduce Locally Running MapReduce on Cluster Packaging MapReduce Jobs MapReduce CLASSPATH Decomposing into MapReduce |
MapReduce Job Using JobControl class Joining data-sets User Defined Functions Logs and Web UI Input and Output Formats Anatomy of Mappers Reducers and Combiners Partitioners and Counters Speculative Execution Distributed Cache YARN Components |
Module 7 : Hadoop Streaming |
Module 8 : Utilities |
Module 9 : Hive |
|
Implement a Streaming Job Contrast with Java Code Create counts in Streaming App Text Processing Use Case Key Value Pairs $yarn command Using Pipes |
ZooKeeper Scoop Introduce Oozie Deploy and Run Oozie Workflow Pig Overview Execution Modes Developing Pig Script |
Hive Concepts Hive Clients Table Creation and Deletion Loading Data into Hive Partitioning Bucketing Joins |
